TA INSTRUMENTS AR-G2

Anton Paar Rheometer


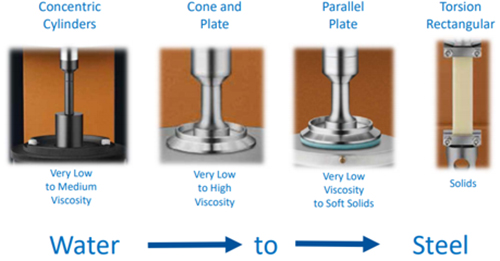
Summary of Technique
Rheometer measures both viscosity and viscoelasticity of fluids, semi-solids and solids. In a rheological measurement stress, strain (shear rate) are all calculated signals. The raw signals behind the scene are torque, angular displacement and angular velocity.
- Viscosity- defined as a materials resistance to deformation and as a function of shear rate or stress with time and temperature dependence.
- Viscoelasticity- is a property of a material that exhibits both viscous and elastic character.
Common testing methods are:
- Stress and strain sweep
- Time sweep
- Frequency sweep
- Temperature ramp
- Temperature sweep
- Stress relaxation
Information Provided
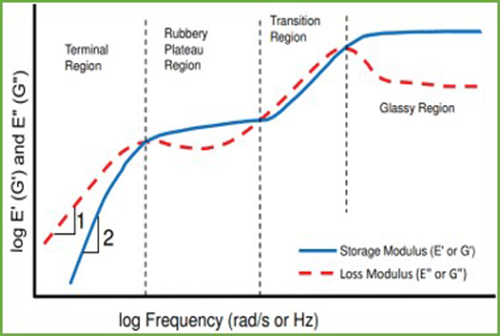
- Los modulus, storage modulus, tan delta with respect to time, temperature, frequency and stress/strain
- Yield stress
- Non-Newtonian viscous behavior
- Thixotropy
- Elasticity
- Stress relaxation
- Viscosity
- Curing rates
- Flow behaviors
- Crosslinking density
- Stability of materials
Lab Location and Contact Information
Location: Thermal Analysis, Rheology, and Polymer Processing Lab
Point of Contact: Dennis Ndaya
dennis.ndaya@uconn.edu
860-486-4075